Transient temperature calculator
This calculator was made for educational purposes only. No rights can be obtained from the results you calculate. If you have comments please contact info@dspe.nl.
References

DSPE appoints Martin van den…
Upon his retirement from ASML, Martin van den Brink was appointed honorary member of DSPE.
Read more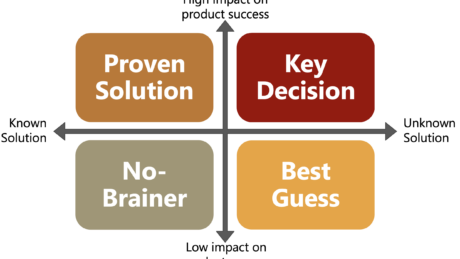
High-velocity innovation
Making crucial design decisions early in the concept phase of a project, may lead to severe cost and time overruns when these decisions are based on assumptions and/or incomplete knowledge.
Read more
Hybrid variable-reluctance actuator technology on-sky
Astronomers use deformable mirrors to improve the image of a telescope by correcting for the optical distortions caused by atmospheric turbulence.
Read more